Return a sample (or samples) from the “standard normal” distribution.
If positive, int_like or int-convertible arguments are provided,
randn generates an array of shape (d0, d1, ..., dn), filled
with random floats sampled from a univariate “normal” (Gaussian)
distribution of mean 0 and variance 1 (if any of the 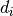 are
floats, they are first converted to integers by truncation). A single
float randomly sampled from the distribution is returned if no
argument is provided.
are
floats, they are first converted to integers by truncation). A single
float randomly sampled from the distribution is returned if no
argument is provided.
This is a convenience function. If you want an interface that takes a
tuple as the first argument, use numpy.random.standard_normal instead.
| Parameters: | d1, .., dn (d0,) – The dimensions of the returned array, should be all positive.
If no argument is given a single Python float is returned. |
|---|
| Returns: | Z – A (d0, d1, ..., dn)-shaped array of floating-point samples from
the standard normal distribution, or a single such float if
no parameters were supplied. |
|---|
| Return type: | ndarray or float |
|---|
See also
random.standard_normal()- Similar, but takes a tuple as its argument.
Notes
For random samples from 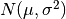 , use:
, use:
sigma * np.random.randn(...) + mu
Examples
>>> np.random.randn()
2.1923875335537315 #random
Two-by-four array of samples from N(3, 6.25):
>>> 2.5 * np.random.randn(2, 4) + 3
array([[-4.49401501, 4.00950034, -1.81814867, 7.29718677], #random
[ 0.39924804, 4.68456316, 4.99394529, 4.84057254]]) #random


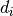 are
floats, they are first converted to integers by truncation). A single
float randomly sampled from the distribution is returned if no
argument is provided.
are
floats, they are first converted to integers by truncation). A single
float randomly sampled from the distribution is returned if no
argument is provided.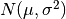 , use:
, use: